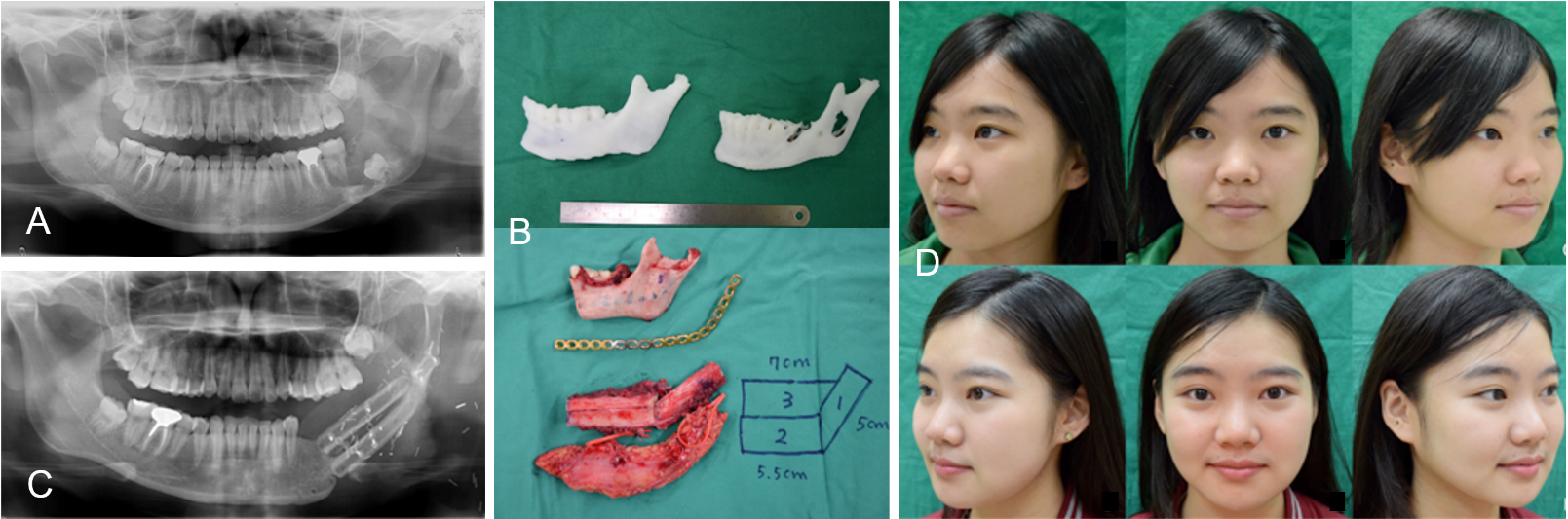
Mandible reconstruction after benign tumor excision usually requires a free vascularized bone graft. However, good cosmetic and functional results are not easy to achieve. The three-dimensional (3D) bio-model is a technique based on computer tomography (CT). The use of this technique in reconstructive surgery has increased in recent years. The patient suffered from an odontogenic keratocyst (OKC) located between the ramus and angle of the left mandible (Panel A). The 3D stereolithography method was used to design a pre-operative bio-model. One model was designed to define the excision margins of the lesion site. The contralateral site served as a mirror to create the template and a second model was printed to preform the reconstructive plate to the mandible (Panel B upper). After tumor excision, a single stage reconstruction was performed with a left free fibula osteoseptocutaneous flap (Panel B lower). At 18 months follow-up, the bone had good union, and the patient showed a good aesthetic result, proper occlusion, and normal masticatory function (Panel C and D). We propose that the 3D bio-model can assist surgeons to evaluate the size of the defect, design osteotomies tailored to the defect, and shaping of the titanium plate to fit the mandible pre-operatively, which shortens the operative time.
Received date: May 08, 2017
Accepted date: May 08, 2017
Published date: May 09, 2017
None
None
Patient consent was obtained for the publication of this case and any accompanying images.
© 2017 The Author(s). This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC-BY).
Yen CI, Chou PY, Hsu ATW, Shafarenko M, Kolios G, Wu CT, Kwon SH, Chen CT, Chang TNJ. Mandible reconstruction by the assistant of stereolithographic three-dimensional printing model technique. Preprint Arch Clin Images Videos 2017;1(2):1. doi:10.24983/scitemed.paciv.2017.00009