In an era of clinical information overload, translating fragmented data into actionable judgment represents a critical challenge for health systems. This article examines the transition of reviews from expert interpretation toward reproducible evidence infrastructure, delineating the complementary roles of narrative reviews, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses in knowledge production. The central argument is that review articles should no longer be classified as secondary literature; rather, they serve as foundational frameworks that recalibrate clinical consensus, identify research gaps, and translate evidence into practice. Central to this shift is a redefined concept of originality, wherein the value of a systematic review derives not from statistical synthesis alone, but from its capacity to objectively expose the limitations of the evidence base. Under rigorous frameworks such as PRISMA and Cochrane standards, high-quality reviews mitigate the risks of "precise illusion" and research waste, providing decision safety in domains where high-certainty evidence is absent. To counter the crisis of mass-produced, low-quality literature, the article emphasizes that methodological rigor must become an ethical baseline, requiring a high-quality review to precede every new clinical trial. Simultaneously, the field must transition from discrete publications to living systematic reviews to eliminate multi-year evidence vacuums. Furthermore, while AI-assisted screening offers efficiency, a "human-in-the-loop" model remains a non-negotiable safeguard against error propagation. This evolution is essential to protecting the integrity of evidence-based medicine.
Within the clinical knowledge ecosystem, review articles occupy a position that appears familiar yet remains frequently undervalued. A review is neither a simple renarration of prior studies nor a textbook-style digest intended for cursory orientation. More precisely, review articles constitute a core component of the evidence infrastructure through which the medical community organizes uncertainty, recalibrates consensus, delineates research gaps, and translates dispersed evidence into usable clinical judgment.
Managing Overload and Controversy
Clinicians, researchers, and policymakers increasingly encounter unmanageable information overload, necessitating systematic integration to support rational decision-making [1]. This requirement is particularly acute in domains where clinical practice is highly contested and definitive therapeutic evidence remains unavailable. In such settings, high-quality review articles provide clinicians and patients with decision pathways of substantial practical value. These syntheses facilitate optimal risk-benefit trade-offs even when the scientific frontier remains indistinct [2].
Sustaining Rigorous Scientific Enterprise
When the value of medical research is defined solely by the generation of primary data, academic systems often misclassify review articles as secondary outputs. However, as guideline development and clinical decision-making increasingly rely on integrated bodies of evidence, the function of these articles has evolved far beyond facilitating literature review. Review articles are essential for sustaining evidentiary rigor, as they employ explicit methods to constrain bias and enhance the accuracy of clinical conclusions [1].
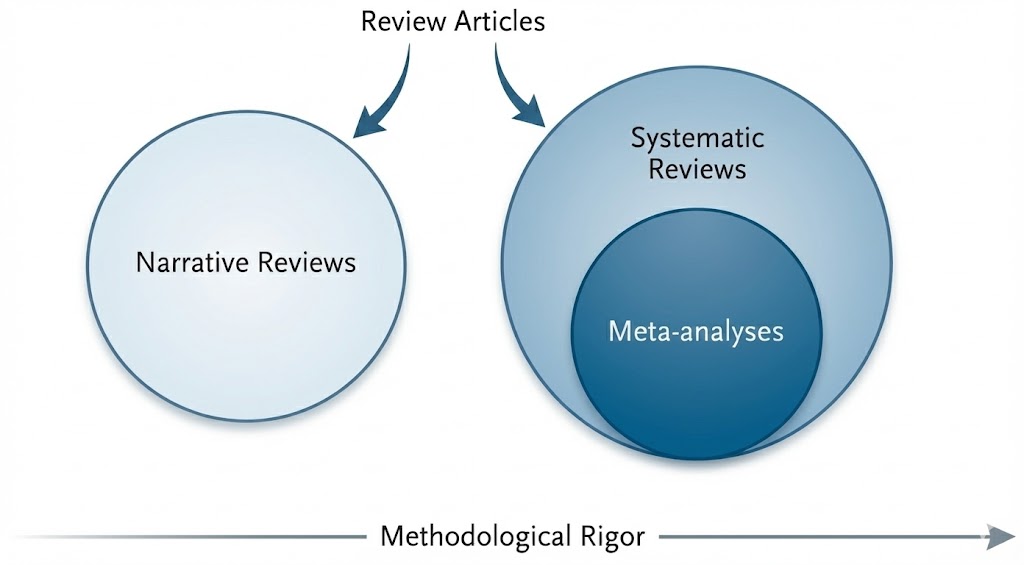
Review articles represent a heterogeneous rather than a monolithic genre; consequently, treating these diverse forms as interchangeable often obscures the evaluative standards appropriate to each. From the perspective of knowledge production, three primary categories are distinguishable: narrative reviews, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses (Figure 1). A systematic review is defined by a prespecified research question, explicit eligibility criteria, a comprehensive search strategy, and critical appraisal of the included evidence [3]. While these methodologies diverge in their technical objectives and levels of reproducibility, they function as complementary tools within clinical medicine. Collectively, these varied approaches reinforce the evidentiary foundation and improve the reliability of clinical decision-making.
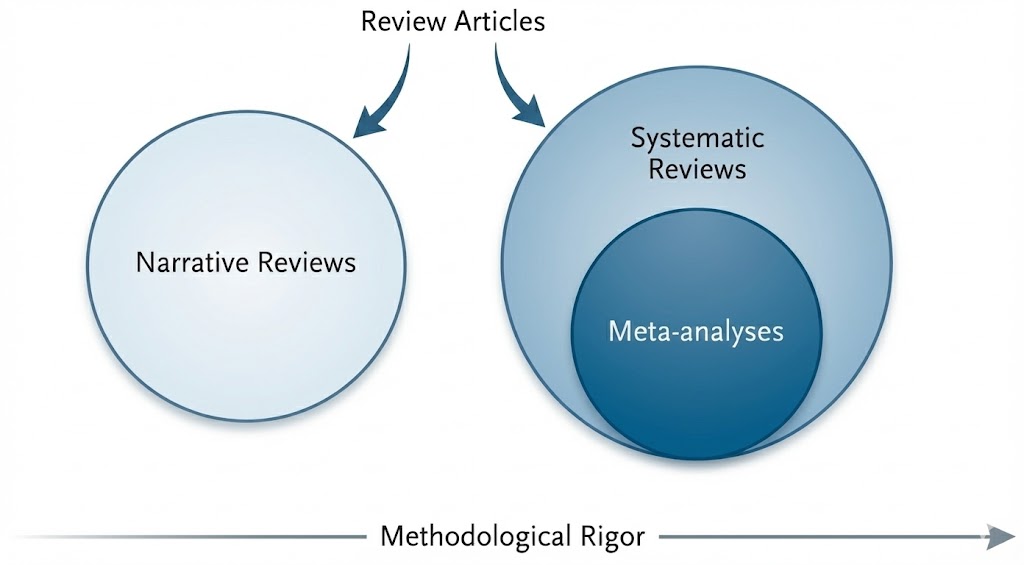
Figure 1. Classification framework and methodological rigor of review articles. This framework illustrates the functional roles and conceptual relationships among review formats. Narrative reviews prioritize expert interpretation and broad context to guide clinical management. Systematic reviews employ standardized protocols and explicit criteria to establish a transparent, reproducible decision chain. Meta-analyses represent a quantitative subset of systematic reviews rather than a separate category. The horizontal axis indicates that methodological rigor increases with adherence to structured procedures and reporting standards.
The primary value of narrative reviews resides in expert interpretation. In rapidly evolving fields where conceptual frameworks remain unsettled, checklist-based evidence aggregation frequently proves insufficient to yield an intelligible synthesis. When clinical questions lack definitive direction, these reviews leverage expert synthesis to provide preliminary integration and propose potential therapeutic solutions. The narrative format facilitates the synthesis of pathophysiologic mechanisms and clinical phenotypes into etiologic models where structured appraisal remains challenging [2,4]. In the absence of high-certainty evidence, these reviews support the development of pragmatic management pathways, which are typically operationalized through structured flow diagrams.
Integrating Biological Scales
Narrative reviews furthermore serve as integrators across biological scales, translating molecular data, including genomic regulation and intracellular signaling cascades, into clinically meaningful explanations of disease behavior. In cholesteatoma, for instance, when traditional anatomic theories fail to account for marked invasiveness and recurrence, high-quality narrative synthesis utilizes molecular evidence to reframe the disorder as a dual imbalance of dysregulated cellular proliferation and exaggerated innate immune activation [5]. By bridging the gap between bench research and clinical phenotypes, this synthesis generates a conceptual framework for the potential development of nonsurgical therapies. This systematic consolidation of complex pathobiology offers a macroscopic perspective that remains beyond the scope of individual experimental studies.
Supporting Clinical Decision Safety
The utility of narrative guidance resides not in a claim to absolute truth but in its capacity to support decision safety within clinical practice. By explicitly framing the objective as risk mitigation rather than definitive proof, narrative synthesis addresses concerns regarding evidentiary weight through practical utility. In settings where high-level evidence is unavailable, expert integration serves as a foundational framework for defining decision thresholds and care pathways.
The management of Eustachian tube dysfunction in children with cleft palate illustrates this methodology [2]. In this clinical scenario, where extensive randomized trials are absent, narrative synthesis establishes legitimacy by integrating foundational anatomic principles with dispersed observational evidence. This integrative approach enables the definition of specific decision thresholds and care pathways derived from professional consensus. By replacing unstructured conjecture with proceduralized clinical reasoning, such guidance prevents ineffective invasive interventions and reduces delays in appropriate patient management. This application demonstrates how expert synthesis provides a robust translational blueprint even when high-certainty evidence is unavailable.
The primary value of systematic reviews is defined by methodological procedure. Systematic reviews translate clinical uncertainty into answerable research questions through the Population, Intervention, Comparator, and Outcomes (PICO) framework [6]. They employ reproducible processes for literature identification, data extraction, risk of bias assessment, and evidence synthesis. A fundamental objective is to appraise benefits and harms with equal weight for specified interventions, such as tympanostomy tube insertion [7]. Through such disciplined protocols, these reviews move beyond simple summation to reveal the specific vulnerabilities and fragilities within the existing evidence landscape.
Transparency and Reproducibility
A systematic review functions as a reproducible decision chain rather than a narrative exercise [6]. Every methodological selection, including search strategies, outcome definitions, and risk of bias instruments, delineates the boundaries of the evidence base and dictates the robustness of the resulting conclusions [8]. This methodological transparency constitutes the foundational attribute that enables independent verification of the synthesis. Peers may scrutinize reported details sequentially to assess the coherence of the decision chain and the completeness of the process. Consequently, such transparency serves as a prerequisite for evaluating both the credibility and the clinical applicability of the findings [9].
Methodological Rigor and Evidence Quality
A fundamental distinction exists between methodological rigor and the intrinsic quality of underlying evidence. Even when employing advanced instruments such as the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) framework [10], evidentiary certainty remains very low if primary data originate from fragile study designs or underpowered cohorts. This distinction illuminates the objective role of systematic reviews, where procedural rigor serves as a diagnostic tool for data quality. Their primary function involves the transparent disclosure of evidentiary limitations rather than the artificial elevation of evidentiary grade through methodological protocols.
This principle is exemplified by research on tympanostomy tube placement in children with cleft palate [7]. Owing to the scarcity of randomized trials in this domain, even the most rigorous systematic methods yield conclusions of very low certainty. Such findings characterize the fragility of the available evidence rather than repudiating the clinical utility of the intervention itself. Consequently, these conclusions necessitate clinical caution, advising against the treatment of such syntheses as definitive authority. Methodological precision cannot substitute for critical vigilance regarding the inherent limits of the evidence base.
Meta-analysis represents a statistical methodology rather than a distinct study classification. Its utility resides in quantitative synthesis, which, under appropriate conditions, enhances inferential precision, increases statistical power, and elucidates sources of heterogeneity [1]. A fundamental distinction persists between the qualitative rigor of a systematic review and the mathematical application of meta-analysis. When primary studies exhibit substantial heterogeneity, poor methodological quality, or a high risk of bias, the imposition of quantitative pooling can generate an illusion of precision. Such forced aggregation risks misleading clinical judgment and contributing to research waste. In such instances, a structured qualitative integration provides a more accurate representation of data quality than does quantitative pooling. This deliberate decision to forgo meta-analysis when primary evidence is insufficient represents an asymmetry in rigor that serves as a core safeguard against the propagation of spurious medical findings [7,11].
The academic value of review articles is frequently underestimated when originality is defined exclusively as the generation of primary data. This narrow definition fails to account for the shifting landscape of contemporary medicine, where the primary scientific bottleneck has transitioned from data acquisition to the capacity to extract signal from an expanding and heterogeneous evidence base. The clinical landscape therefore demands not only an increased volume of research but also higher inferential reliability to guide practice. Because individual study findings are potentially erroneous [12], systematic integration is essential to validate, contextualize, and recalibrate established scientific tenets.
Although the degree of this original contribution varies among different review formats, it is most rigorously manifested in systematic reviews. By applying a transparent decision chain to redefine the boundaries of the evidence base, systematic reviews elevate synthesis from a descriptive exercise to a reproducible research methodology. This rigorous process can revise prevailing consensus and, even when utilizing existing primary studies, lead to materially different clinical conclusions [13]. High-quality evidence synthesis thus represents an original scholarly contribution, functioning not as a substitute for primary research but as the essential mechanism that renders such research interpretable and dependable in clinical practice.
Institutional Legitimacy of Systematic Reviews
The institutional standing of systematic reviews has been elevated within the academic hierarchy. Within the editorial landscape, 71% of editors-in-chief at core clinical journals now categorize high-quality systematic reviews as original research [14]. Concurrently, 47% of biomedical doctoral programs in Europe formally accept systematic reviews as primary components of dissertation work [15]. These developments signify a systemic transition toward recognizing systematic synthesis as a rigorous and original contribution to scientific discourse. Consequently, systematic reviews are now integrated into the formal structures of academic training and degree evaluation, achieving a legitimacy recognized by both editorial and educational authorities.
Evidence Mapping and Trial Design
High-quality review articles contribute original scientific value by mapping the evidence landscape to define the boundaries of current knowledge. Through a comprehensive evaluation of the literature, these reviews identify specific deficiencies in primary research and characterize areas where clinical evidence remains inconclusive. This mapping distinguishes between clinical questions prepared for definitive testing and those requiring further foundational investigation. Such a diagnostic function extends beyond a rudimentary acknowledgment of data scarcity. By synthesizing available evidence, reviews establish a rigorous scientific foundation that informs the design and execution of subsequent prospective studies, including randomized trials [4,7].
Surgical Precision and Review Originality
Beyond their role in defining knowledge boundaries, high-quality reviews provide an additional original contribution by integrating surgical reasoning with clinical outcomes to evaluate, rather than merely reinforce, established protocols. By synthesizing long-term experience alongside comparative results, these reviews can potentially support individualized operative decisions when disease heterogeneity renders a single standardized procedure inadequate. Instead of applying a universal operative standard to complex pathologies, this approach promotes flexible strategies that align the extent of resection with the anatomic location of the disease. This methodology aims to minimize procedural morbidity while ensuring durable clearance. By weighing the trade-offs between various techniques and formalizing the logic behind procedure selection, reviews can generate patient-centered decision algorithms that complement the specific validation offered by individual trials. Consequently, a comprehensive review serves as a clinical framework that translates heterogeneous data into a coherent model for use at the point of care.
This perspective is illustrated by contemporary management strategies for acquired cholesteatoma [16]. Rather than being restricted to the traditional dichotomy between canal-wall-up and canal-wall-down procedures, investigators have proposed an extent-guided excisional pathway. This approach defines the scope of resection according to the actual anatomic spread of the disease, shifting procedure selection from technical convention toward contextualized decision-making. The originality lies in the synthesis itself, which provides a framework for surgeons to evaluate options and select procedures even when high-certainty comparative evidence is limited. Such evidence-based logic, developed through rigorous synthesis, directly addresses the misconception that review articles lack original scientific merit.
The hierarchy of evidence is traditionally conceptualized as a pyramid, reflecting the transition in medicine from experience-based practice toward evidence-based principles. At its foundation, expert opinion and mechanistic inference provide essential clinical insights but remain inherently vulnerable to subjective bias. Narrative reviews serve as a comprehensive interpretive bridge within this structure by synthesizing primary clinical studies with mechanistic theories and expert insights to provide a holistic framework for complex clinical questions. Above this foundational synthesis, intermediate tiers comprise case-control and cohort studies, which utilize increasingly standardized observational designs to strengthen causal inference.
As the hierarchy ascends, randomized controlled trials serve as the reference standard for estimating treatment effects because random assignment minimizes confounding. At the apex, systematic reviews and meta-analyses integrate findings across multiple investigations to provide the most reliable quantitative estimates for clinical practice [3,17]. Consequently, while review articles occupy different levels of the pyramid depending on their methodological rigor, they collectively represent the essential integrative layers that transform primary data into a coherent and actionable body of medical knowledge.
Data Ceiling in Synthesis
While analytical frameworks add methodological rigor, a fundamental constraint persists: the quality of any review is inextricably linked to the quality of its underlying data. Procedural standards may mitigate execution-related bias, yet they lack the capacity to compensate for inherent flaws in primary research. Whether a review follows a narrative or systematic format, its conclusions remain strictly limited by the fragility of the included evidence [8]. Failure to recognize this data ceiling risks misinterpreting the synthesis as a validation of clinical certainty when it should instead be viewed as an assessment of evidence quality. Accordingly, review articles should not be regarded as mechanisms that transform weak evidence into robust conclusions. Instead, high-quality synthesis serves as a diagnostic instrument that makes the boundaries and uncertainties of the evidence base explicit.
Ethical Mandate for Evidence Synthesis
The rapid proliferation of review articles poses a significant challenge to academic integrity. Reviews produced primarily to satisfy publication metrics consistently lack focused clinical inquiries and yield discordant results [18,19]. This misalignment between research output and clinical utility accelerates a cycle of systemic inefficiency. Seminal analyses indicate that cumulative waste across the stages of study design, publication, and reporting leads to the loss of more than 85% of global research investment [19]. Consequently, the dividends from tens of billions of dollars in annual funding are diminished by correctable methodological failures.
This systemic waste typically begins at the design stage, where over 50% of studies are initiated without reference to existing systematic assessments [19]. Such methodological neglect prevents new investigations from being properly situated within the established evidence base. Within this environment, rigor in synthesis represents an ethical necessity. Before commencing new primary research, investigators have a professional obligation to conduct high-quality reviews to map the evidence landscape accurately. This practice facilitates the responsible allocation of scientific resources and serves as a critical safeguard for trial participants by preventing exposure to redundant risks or ineffective interventions. By identifying gaps and uncertainties, researchers justify new trials as both ethically sound and scientifically substantial.
Narrative reviews have historically faced criticism for inherent subjectivity. Initial guidelines, including those proposed by Green and Johnson (2006) [20] and Gasparyan et al. (2011) [21], underscored the necessity of transparent search processes within narrative formats [20,21]. Nevertheless, these recommendations functioned primarily as expert consensus and lacked a validated instrument for quality appraisal. The introduction of the Scale for the Assessment of Narrative Review Articles (SANRA) in 2019 established a structured framework that significantly reduced reliance on individual author discretion [22]. This shift signifies a formal transition from experience-informed writing toward a scientifically rigorous methodology characterized by explicit reporting criteria. By necessitating the systematic disclosure of search strategies, evidence selection, and inferential logic, these standards ensure that scholarly insight rests on a verifiable and transparent literature base.
Methodological Foundations of Meta-Analytic Reporting
In contrast to narrative reviews, systematic reviews and meta-analyses adhere to an established methodological tradition. This tradition mandates high levels of reproducibility and transparency. The maturation of these standards was significantly advanced by the Quality of Reporting of Meta-analyses (QUOROM) statement in 1999 [23]. Although QUOROM focused explicitly on quantitative reporting for meta-analyses of randomized trials, it formalized the procedural transparency essential for systematic synthesis. This transition established that scientific validity depends upon traceable methodologies rather than solely upon statistical accuracy.
Evolution of Systematic Reporting: PRISMA Framework
Scientific integrity is predicated equally upon the transparency of selection processes and the rigor of statistical computation. Consequently, the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) statement was introduced in 2009 [24]. This framework expanded the methodological focus beyond quantitative pooling to encompass the entire systematic review workflow. PRISMA requires investigators to disclose the complete decision chain. This disclosure includes every stage from literature identification to the formal assessment of the risk of bias.
Cochrane Operational Standards
Cochrane has established the definitive methodological standards and handbook guidance for the execution of evidence syntheses [6]. This framework prioritizes rigorous conduct in systematic reviews and, where appropriate, meta-analyses. Key components of these standards include structured assessments of the risk of bias in primary studies and the judicious selection of analytical models to manage clinical and statistical heterogeneity. Furthermore, Cochrane specifies formal procedures for periodically evaluating whether reviews require updates in response to emerging evidence or methodological advancements.
In contrast, PRISMA serves as a reporting guideline designed to ensure the transparency and completeness of published syntheses. Accordingly, PRISMA primarily targets the structure of the final report, whereas Cochrane guidance defines the operational expectations for the research process itself. This functional distinction ensures that while PRISMA facilitates the auditability of a study, Cochrane standards promote procedural consistency. By adhering to these integrated protocols, investigators minimize avoidable subjectivity and maintain scientific integrity when synthesizing complex bodies of evidence.
Conditional Endorsement and Evidentiary Limits
Both PRISMA reporting standards and Cochrane operational procedures reflect the principle of conditional endorsement. Under even the most rigorous frameworks, the validity of clinical conclusions remains limited by the quality of the underlying evidence. Methodological standards are not intended to obscure deficiencies in the data. Instead, these standards serve to define the specific boundaries of what the evidence can support. The transparent representation of such uncertainty is a fundamental contribution of review articles to clinical decision-making. By identifying these limitations, high-quality reviews prevent the over-interpretation of inconclusive data and help establish priorities for future research.
Contemporary review literature is undergoing a fundamental evolution from static, single-point publications into dynamic knowledge infrastructure, anchored by the PRISMA 2020 reporting framework to ensure rigorous transparency and structural integrity [8,9]. Conventional review articles function as discrete products with workflows that terminate upon publication. Conversely, living systematic reviews (LSRs) reconceptualize evidence synthesis as a continuous operational system. To maintain scientific validity during this perpetual update cycle, the PRISMA-LSR extension provides the necessary methodological scaffolding for reporting version-controlled evidence and monitoring real-time data accrual [25]. This evolution shifts the primary value of review articles from retrospective organization toward active version management and the iterative alignment of emerging data with established conclusions.
This transition addresses significant temporal limitations in current literature. In a bibliometric analysis of 1,000 PubMed-indexed, full-text, English-language biomedical research articles, Díez-Vidal and Arribas found a mean citation lag of 5.53 years for works described as "recent" [26]. Furthermore, 17.7% of citations labeled as "recent" were at least 10 years old. These findings demonstrate that the term "recent" often functions as a flexible rhetorical device rather than a precise temporal marker. Recasting review articles as dynamic infrastructure seeks to eliminate the multi-year evidence vacuum caused by these reporting delays.
Automated workflows now serve as essential components for maintaining real-time evidence surveillance. Ge et al. reported that screening assisted by large language models, specifically ChatGPT v4.0, achieved a specificity of 96% and a sensitivity of 93% for study identification [27]. Such performance significantly reduces the marginal costs associated with continuous monitoring. Nevertheless, fully automated pipelines introduce meaningful risks of error propagation. When the review process is conceptualized as five standard stages, even a 5% error rate at each stage can compound to reduce overall accuracy to approximately 81.5% [27].
Consequently, the objective of building knowledge infrastructure requires implementing expert oversight through a human-in-the-loop model rather than the total removal of human investigators. In this framework, automation does not replace clinical judgment but instead operationalizes auditable and reproducible decision chains. This approach preserves scientific rigor while amplifying expert capacity, ensuring that evidence integration advances in synchronization with ongoing discovery.
Review articles have evolved into a vital evidence infrastructure that updates clinical consensus and identifies research gaps. By establishing clear decision chains, these reviews improve patient safety. As research fragmentation increases waste, high-quality reviews must precede new trials to ensure they are scientifically and ethically justified. This step protects participants from unnecessary risks and sets a rigorous standard for clinical research. Moving forward, living reviews and AI automation, guided by human experts, aim to combine scientific rigor with real-world utility. Collectively, these systems provide a reliable foundation for precision medicine.
Received date: November 20, 2025
Accepted date: December 11, 2025
Published date: December 23, 2025
The manuscript has not been presented or discussed at any scientific meetings, conferences, or seminars related to the topic of the research.
The study adheres to the ethical principles outlined in the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its subsequent revisions, or other equivalent ethical standards that may be applicable. These ethical standards govern the use of human subjects in research and ensure that the study is conducted in an ethical and responsible manner. The researchers have taken extensive care to ensure that the study complies with all ethical standards and guidelines to protect the well-being and privacy of the participants.
The author(s) of this research wish to declare that the study was conducted without the support of any specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. The author(s) conducted the study solely with their own resources, without any external financial assistance. The lack of financial support from external sources does not in any way impact the integrity or quality of the research presented in this article. The author(s) have ensured that the study was conducted according to the highest ethical and scientific standards.
In accordance with the ethical standards set forth by the SciTeMed publishing group for the publication of high-quality scientific research, the author(s) of this article declare that there are no financial or other conflicts of interest that could potentially impact the integrity of the research presented. Additionally, the author(s) affirm that this work is solely the intellectual property of the author(s), and no other individuals or entities have substantially contributed to its content or findings.
It is imperative to acknowledge that the opinions and statements articulated in this article are the exclusive responsibility of the author(s), and do not necessarily reflect the views or opinions of their affiliated institutions, the publishing house, editors, or other reviewers. Furthermore, the publisher does not endorse or guarantee the accuracy of any statements made by the manufacturer(s) or author(s). These disclaimers emphasize the importance of respecting the author(s)' autonomy and the ability to express their own opinions regarding the subject matter, as well as those readers should exercise their own discretion in understanding the information provided. The position of the author(s) as well as their level of expertise in the subject area must be discerned, while also exercising critical thinking skills to arrive at an independent conclusion. As such, it is essential to approach the information in this article with an open mind and a discerning outlook.
© 2025 The Author(s). The article presented here is openly accessible under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC-BY). This license grants the right for the material to be used, distributed, and reproduced in any way by anyone, provided that the original author(s), copyright holder(s), and the journal of publication are properly credited and cited as the source of the material. We follow accepted academic practices to ensure that proper credit is given to the original author(s) and the copyright holder(s), and that the original publication in this journal is cited accurately. Any use, distribution, or reproduction of the material must be consistent with the terms and conditions of the CC-BY license, and must not be compiled, distributed, or reproduced in a manner that is inconsistent with these terms and conditions. We encourage the use and dissemination of this material in a manner that respects and acknowledges the intellectual property rights of the original author(s) and copyright holder(s), and the importance of proper citation and attribution in academic publishing.
AI is rapidly evolving from a supportive tool into a core component of medical decision making and evidence synthesis, reshaping how clinicians interpret information at the point of care. Yet, while much of medical AI research emphasizes algorithmic performance and explainability, it seldom addresses the more practical question: how should physicians evaluate an AI recommendation in real-world, high-risk situations when fluent outputs can conceal critical errors. This Perspective offers a clinician-centered framework that treats AI outputs as provisional, testable hypotheses rather than definitive conclusions. By guiding users through premise verification, terminological precision, evidence appraisal, and causal analysis, it provides a structured defense against hallucinations, selective reporting, and data poisoning, using otolaryngology as a high-stakes, multimodal model. By placing clinical judgment at the center of AI use, this work shifts the field from passive automation toward safer, more accountable decision support grounded in patient safety.
This manuscript reframes medical review articles as evidence infrastructure that corrects consensus and maps research gaps, rather than as mere expert commentary. Using cholesteatoma, it contrasts the cross scale synthesis enabled by narrative reviews with the reproducibility of systematic reviews and the methodological limits of meta analysis, and argues that AI enabled automation must remain human in the loop to prevent error propagation. Reviewers find the perspective forward looking but request clearer operationalization, including a quantifiable originality weighting framework, a standardized approach to integrating expert judgment, and a concrete human in the loop workflow with explicit decision rules. The manuscript is publishable in principle, but revision should close the concept to implementation gap by defining a transparent and auditable decision chain, an implementable operating model, an adoption strategy with version control, and verifiable standards that convert the thesis into a deployable reform blueprint.
ResponseThank you for the careful evaluation of my manuscript. I have revised the manuscript in accordance with the reviewers’ comments, and I hope the revised version satisfactorily addresses the requested changes.
This article reframes review scholarship as core infrastructure for medical knowledge production, arguing that originality can arise not only from new data generation but also from reproducible evidence synthesis and coherent research frameworks. Using cholesteatoma pathology as an example, it shows how narrative reviews can translate molecular signals into clinically meaningful explanations and guide fields in which paradigms remain unsettled. The main limitations are the absence of an operational method to weight originality and insufficient detail on how expert clinical judgment is integrated with transparent, rigorous search and selection procedures to address concerns about subjectivity in evidence based medicine. With these points clarified, the manuscript would be well positioned for publication.
This manuscript provides a timely critique of evidence synthesis by framing systematic reviews as core research infrastructure and warning against uncritical automation, particularly the cumulative risk of AI driven error propagation. The concepts of Precise Hallucinations and Asymmetric Rigor are useful and appropriately position investigators as stewards of clinical validity, and the cross scale linkage between molecular mechanisms and disease behavior strengthens the rationale for narrative synthesis. However, the paper remains insufficiently operational: the human in the loop workflow lacks explicit standards, the decision logic for moving from quantitative to qualitative synthesis is under specified, and the proposed institutional implementation requires clearer feasibility grounded mechanisms across heterogeneous research systems.
Kuo CL